1.sql性能下降原因
1.执行时间长;
2.等待时间长。
主要分:查询写的烂,索引失效,关联查询太多join,服务器调优及各种参数配置。
2.sql执行加载顺序
1.用户编写的sql执行顺序
<select_list>
FROM
<left_table> <join_type>
JOIN <right_table> ON <join_condition>
WHERE
<where_condition>
GROUP BY
<group_by_list>
HAVING
<having_condition>
ORDER BY
<order_by_condition>
LIMIT
<limit_number>
2.系统实际的执行顺序
FROM
<left_table> <join_type>
JOIN <right_table> ON <join_condition>
WHERE <where_condition>
GROUP BY <group_by_list>
HAVING <having_condition>
SELECT
DISTINCT <select_list>
ORDER BY
<order_by_condition>
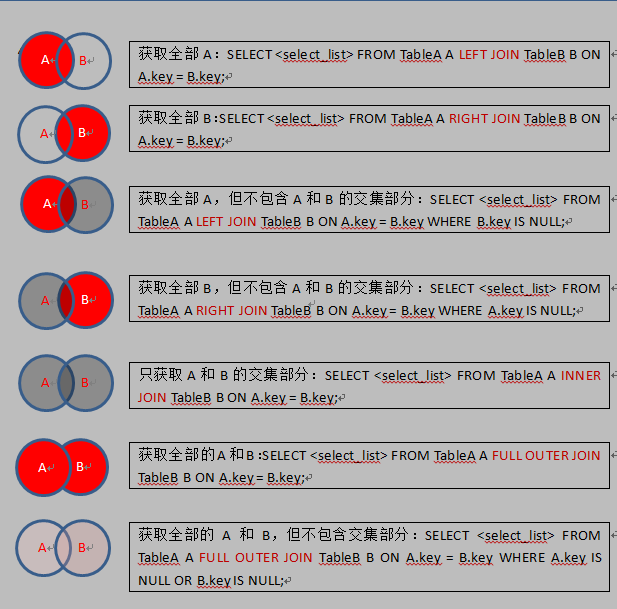
3.mysql的join查询
4.索引
1.索引的定义
索引是用于帮助MYSQL高效获取数据的数据结构,简单理解为排好序的快速查找数据结构。 一般来说索引本身也很大,不可能全部存在内存中,因此索引往往以索引文件的形式存储在磁盘上。
2.索引的优劣
索引的优势:提高数据的检索效率,降低数据库的IO成本,通过索引列队数据进行排序,降低数据对排序的成本,降低了CPU的消耗。
索引的劣势:索引占表空间,降低更新表的速度。
3.索引的分类
单值索引:一个索引只包含单个列,一个表可以有多个单列索引。
唯一索引:索引列的值必须唯一,但允许有空值。
复合索引:一个索引包含多个列。
4.索引的操作命令
创建:create [unique] index indexName on mytable[columnName];
修改:Alter mytable add [unique] index [indexname] on (columnname);
删除:drop index [indexname] on mytable;
查看:show index from mytable;
5.B-Tree索引原理
将数据分成n叉树
5.性能优化
1.Mysql常见瓶颈
CPU:CPU在饱和的时候一般发生在数据装入内存或从磁盘读取内存的时候;
IO:磁盘I/O瓶颈发生在装入数据远大于内存容量的时候;
服务器硬件性能的瓶颈。
2.Explain:
作用:查看执行计划。使用explain关键字可以模拟优化器执行sql查询语句,从而知道mysql时如何处理你的sql语句的。通过它可以看出:
表的读取顺序;
数据读取操作的操作类型;
哪些索引可以使用;
哪些索引被实际使用;
每张表有多少行被优化器执行;
表之间的引用;
用法:explain + 执行的sql
结果分析:
Id:sql的执行顺序,因为一个查询会包含多张表或者嵌套查询,分析结果就会出现多个id(查询你语句),id越大越先被执行,
id相同从上往下执行;
SelectType:包括simple(简单的select,查询中不包含子查询或者union)、primary(查询中包含子查询,
则最外层成为primary,最后加载)、Subquery(在select或者where中包含了子查询)、
Derived(在from列表中包含的子查询被标记为derived,即衍生)、Union result : 从union表获取结果的select、
Union(若第二个select出现在union后,则被标记为union;若union包含在from子句的子查询中,外层select被标记为derived).
Type:级别分为system->const->eq_ref->ref->range->index->all 。一般来说至少达到rang和ref级别。
System:表只有一行记录(等于系统表)、
Const:只通过一次索引就找到了,相当于主键索引(primary key),即where条件是主键。Where id =10;
eq_ref:唯一性索引扫描,对于每个索引键,表中只有一条记录与之匹配。常用于主键和唯一索引扫描。Where idcard = ‘4509’;
Ref:非唯一性索引扫描,返回匹配某个单独值的所有行。比如where age =10;
Range:只检索给定范围的行,key显示使用了哪种索引,一般是where后面出现between、<、>、in等。比如:where age between 30 and 60;
Index:扫描了所有的索引树,比如select id from t;
All:全表扫描。
6.索引优化
1.单表
常用创建联合索引,索引组合为把where用到的判断都加上.
查询语句:Select id from article where category_id=1 and coments >1 order by views desc limit 1.;
初步创建的索引:create index idx_article_ccv on article(category_id,coments,views);
注意:这样建会使得views用不上索引,因为中间的comments有个排序,range类型查询字段后面的索引无效。导致extra中出现fileSort.
提升索引:create index idx_article_cv on article(category_id ,views);
2.两表
相反加索引
比如a left join b on a.carid = b.carid,则索引添加在b表的cardid上;
比如a right join b on a.carid = b.carid,则索引添加在a表的cardid上。
这是由连接特性决定的,left join 用于从右表搜索,左边一定都有
3.三表
Select *from calss left join book on cass.cardid = book. cardid left join phone on book. Cardid = phone .id
则索引的创建为在book表的cardid和phone表的cardid分别创建索引。
4.总结
1.尽量减少join语句中的nestedLoop循环总次数:即使用小表催动大表(EXPLAIN 结果中,第一行出现的表就是驱动表(Important!))
2.优先优化内层循环。比如:括号里面的。
3.保证join语句中被驱动表上join条件字段已经加上索引。
7.索引失效

举例:前提条件组合索引(name,age,position)
1.全值匹配我最爱
Select *from staff where name ='xie'
Select *from staff where name ='xie' and age = 25
Select *from staff where name ='xie' and age = 25 and position = 'man'
以上查询语句索引都会有效
2.最佳左前缀法则
如果索引了多列,要遵守最左前缀法则。意思是:查询你要从索引的最左前列开始并且不跳过索引的列。
Select *from staff where name ='xie';
Select *from staff where age = 25 ;
Select *from staff where age = 25 and position = 'man' ;
Select *from staff where name =’xie’ and position = 'man':
索引1会生效,但是索引2和3会失效,4只会部分用到。
3.不要在索引列上进行任何操作
包括计算、函数、自动或手动的类型转换。
4.存储引擎不能使用索引范围条件右边的列
Select *from staff where name =’xie’ and age =>25 and position = ’man’
在该语句中name和age会用到索引,但是position的索引会失效,因为name用了范围条件。
5.尽量使用覆盖索引
只访问索引的查询(索引列和查询一致),避免select*
比如建立的联合索引(name,age,position),而且查询语句为:
Select name,age,position from staff where name =’xie’ and age = 25 and position = 'man':
这样会更高效,因为explain时,extra中会出现using index。
特别的地方:Select name,age,position from staff where name =’xie’ and age > 25 and position = 'man';
这种写法中age的索引也会失效。
6.使用不等于(!= 或 <>)会使索引失效
比如 :Select *from staff where name !='xie'; 索引会不起作用
7.使用is null 或者 is not null会使索引失效
比如:Select *from staff where name is null; 索引会不起作用
8.like通配符开头(’%abc..’)会使索引失效
比如:Select *from staff where name like '%xie%'; 索引会不起作用
比如:Select *from staff where name like '%xie'; 索引会不起作用
比如:Select *from staff where name like 'xie%'; 索引会起作用,类型为range
解决 like ‘%字符串%’ 索引失效的办法:使用覆盖索引。
比如创建联合索引(name,age),则以下语句都会用到索引:
Select id from staff where name like '%xie%';
Select name from staff where name like'’%xie%';
Select id,name,age from staff where name like '%xie%';
Select name,age from staff where name like '%xie%';
9.字符串不加单引号,索引会失效
因为产生了隐式的类型转换
10.少用or,用它来连接时索引会失效
Select *from staff where name ='xx' or name ='yy'; 索引会不起作用。
Select *from staff where name ='xx' or age >10;索引会不起作用。





